Future of the Universe
Blog
The STAR VIBE satellite was launched in early 2023, with a mission to demonstrate two systems - the Small Telescope for Advanced Reconnaissance and the Vision Inspection Boom Experiment. Scanway is carrying out these mission with German partner German Orbital Systems (GOS), which is responsible for the satellite's structure.

Progress of the mission
STAR VIBE has been launched into sunsynchronous orbit more than 500 kilometers above sea level. Such an orbit ensures that the satellite flies over a given location at the same solar time, making it possible to take images under identical lighting conditions, which in turn helps to compare the collected data over time and draw conclusions.
For more than six months, Scanway engineers conducted a commissioning campaign of all systems, their calibration, as well as testing. The goal of the mission was to raise the TRL (technology readiness level) to the ninth level, which means that the technology is ready to be deployed in the market as a full-fledged product.
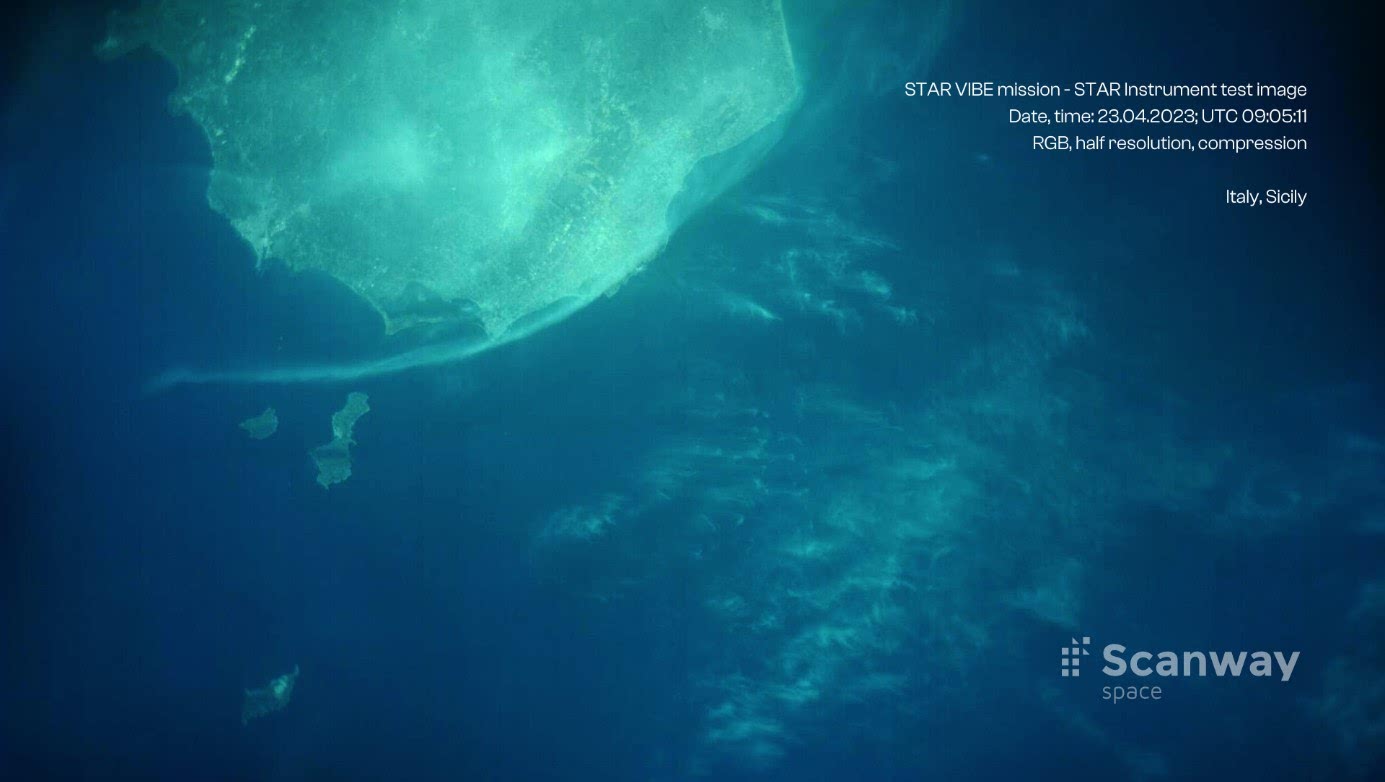
Since the start of the mission, 200 communication sessions have been held, 20 imaging sessions have been conducted and more than 80 images have been obtained, including from areas in Ukraine, Australia, Italy, Iran and other countries. Thus, the mission's key objectives have been achieved, and the mission has been extended by 12 months. These are the most accurate images of Earth from space ever taken by a Polish optical instrument.

Bright “stars” of the mission
It is worth taking the time to learn about the innovative systems being tested - the STAR telescope and the VIBE system.
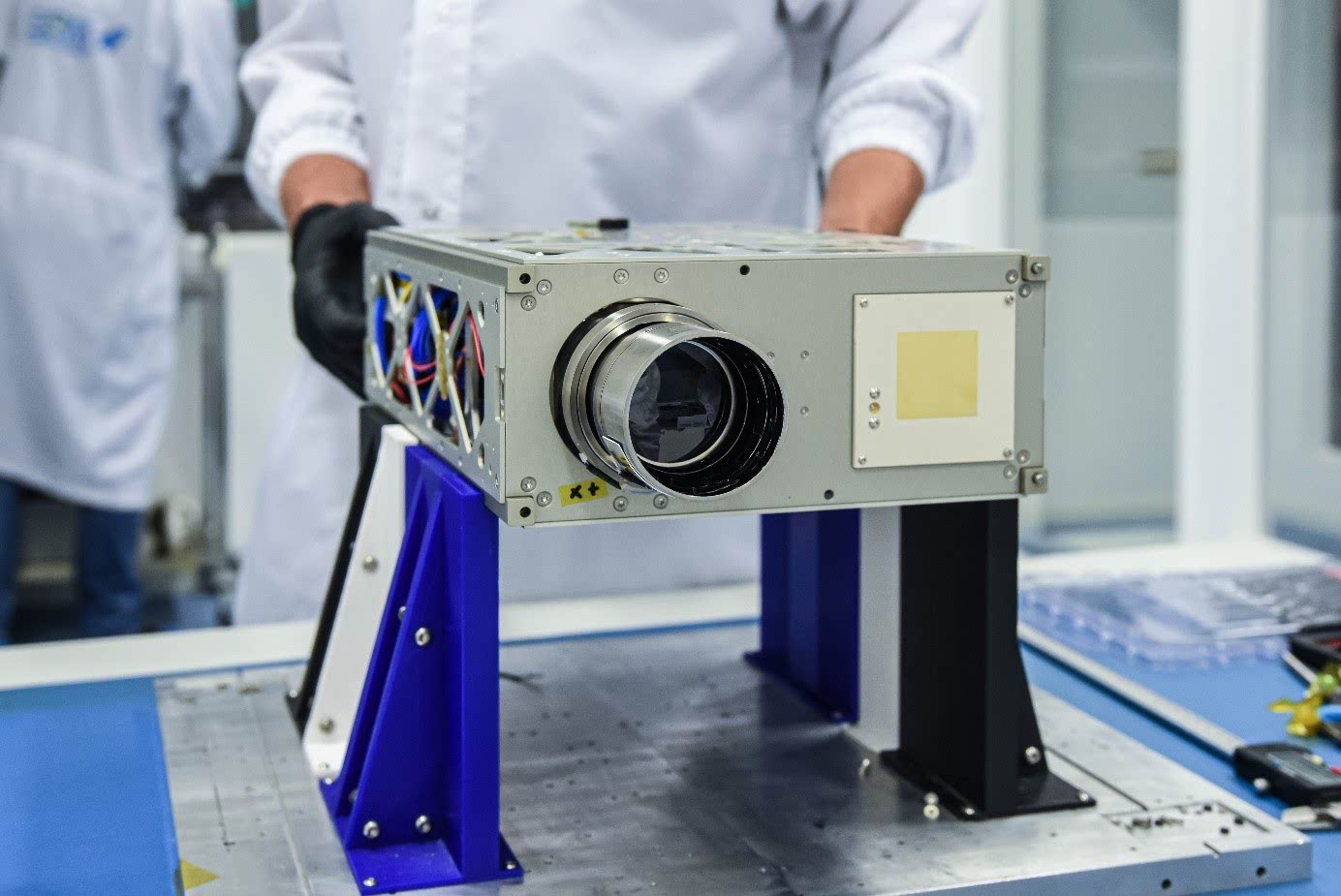
STAR telescope operating in the visible light spectrum. It can take images with a resolution of 25 meters per pixel and provides a large field of view (102.4 x 76.8 km), which enables rapid data collection for a wide variety of purposes, such as natural disasters, climate change or data supporting efficient agriculture, for example. Comparing data collected at different moments in time makes it possible to detect changes.
Despite its extensive capabilities, the telescope itself is not large - it fits in a cuboid measuring 210x77x100 mm (that is, it is 2U in size), and weighs only 1.2 kg.
VIBE system is one of the configurations of Scanway’s product SHS - Spacecraft Health Scanner, which is a system for self-inspection of satellites and rockets. The advanced system is based on the basis of artificial intelligence, which, by collecting data from sensors and cameras, is able to detect potential damage to the observed component. Data analysis takes place in orbit, eliminating the need to use a data link for the analysis itself.
To be more precise, VIBE is an optical system for autonomous diagnostics of the satellite - it is a camera located on a deployable beam. It is connected to an on-board computer, which stores images and enables data analysis by means of artificial intelligence, which, for example, will detect newly formed damage to solar panels.

Future plans
During the mission, Scanway's engineers obtained a lot of data and learned many lessons that help them prepare for the next mission. The EagleEye telescope, which will be placed in a very low orbit - about 350 km - is expected to be launched within the next year. EagleEye is the largest telescope developed in our country, and allows observations in visible light.
What's more, the SHS system is being further developed and will find its application in the upcoming next version of the European Space Agency's rocket - Ariane 6. During the inaugural flight of this rocket, Scanway's system will be tasked with observing and confirming the correct separation of the rocket's fairings and the release of CubeSat.
